A Clear Guide to Pulsatile Tinnitus
Medical Assessment and Care for Pulsatile Tinnitus
Hearing a rhythmic sound that matches your heartbeat can feel alarming, but pulsatile tinnitus is often linked to benign blood-flow changes or middle-ear factors rather than serious illness. Urgent audiovestibular assessment is needed if it starts suddenly, worsens rapidly, follows a head injury, or occurs with neurological symptoms, visual changes, or severe headache.
Comprehensive Care for Hearing, Vertigo & Balance
Comprehensive Care for Hearing, Vertigo & Balance
Rhythmic Vascular Signals
An Overview of Pulsatile Tinnitus
Pulsatile tinnitus is a form of tinnitus where the sound has a rhythmic quality, often in time with the heartbeat. People may notice a whooshing, thumping, or pulsing noise in one or both ears, or sometimes centrally in the head. Unlike more common tinnitus, this sound is usually linked to blood flow or pressure changes rather than the auditory system alone.
In many cases, pulsatile tinnitus relates to benign causes such as altered blood flow near the ear, changes in blood pressure, middle-ear conditions, or increased awareness of normal vascular sounds. However, because it reflects vascular activity, it always requires careful audiovestibular assessment to understand the source and exclude less common but important causes.
Pinpointing the Cause
Diagnosing Pulsatile Tinnitus
When to Get Checked
You should get assessed if pulsatile tinnitus starts suddenly, becomes constant, or is clearly synchronised with your heartbeat, particularly if it is heard in one ear only. New onset following head injury, infection, or surgery also warrants prompt audiovestibular review.
You should seek urgent assessment if it occurs with severe or unusual headache, visual disturbance, facial weakness, neurological symptoms, or raised blood pressure, or if the sound is progressively worsening. Early evaluation helps identify vascular causes and guides appropriate investigations and referrals.
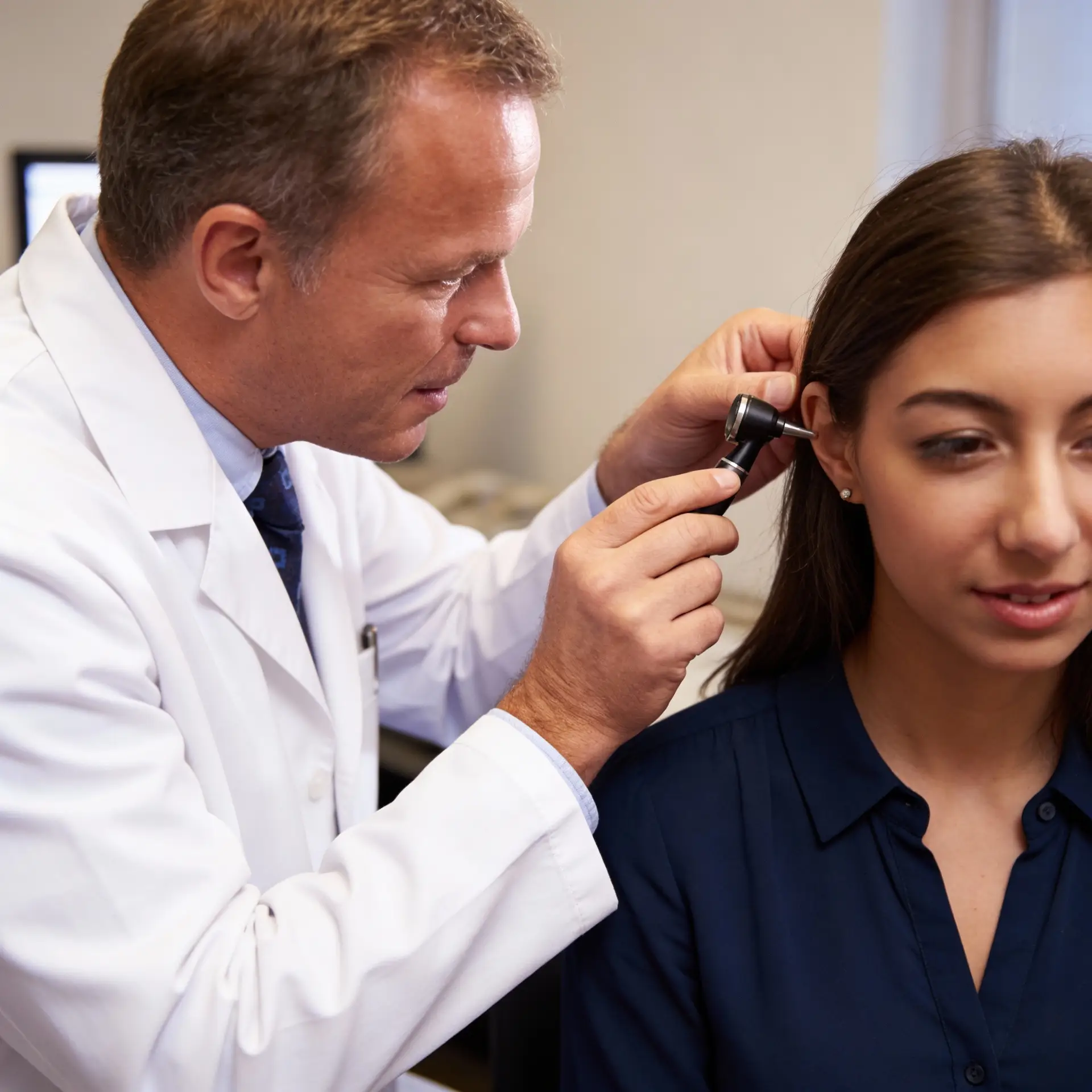
How We Assess Pulsatile Tinnitus
At Harley Audiovestibular Clinic, assessment begins with extended time spent with a senior audiovestibular physician. We focus on understanding the rhythm, onset, and behaviour of the sound, how it relates to heartbeat or posture, and whether it changes with activity. We review hearing, balance, neurological symptoms, medical history, medications, and cardiovascular factors in detail.
Based on this consultation, we plan appropriate investigations. These may include comprehensive hearing tests, middle-ear assessment, and targeted audiovestibular examinations. Where needed, we recommend further medical tests or imaging. Our structured approach ensures concerns are addressed thoroughly and safely.

Major Insurance Providers Accepted
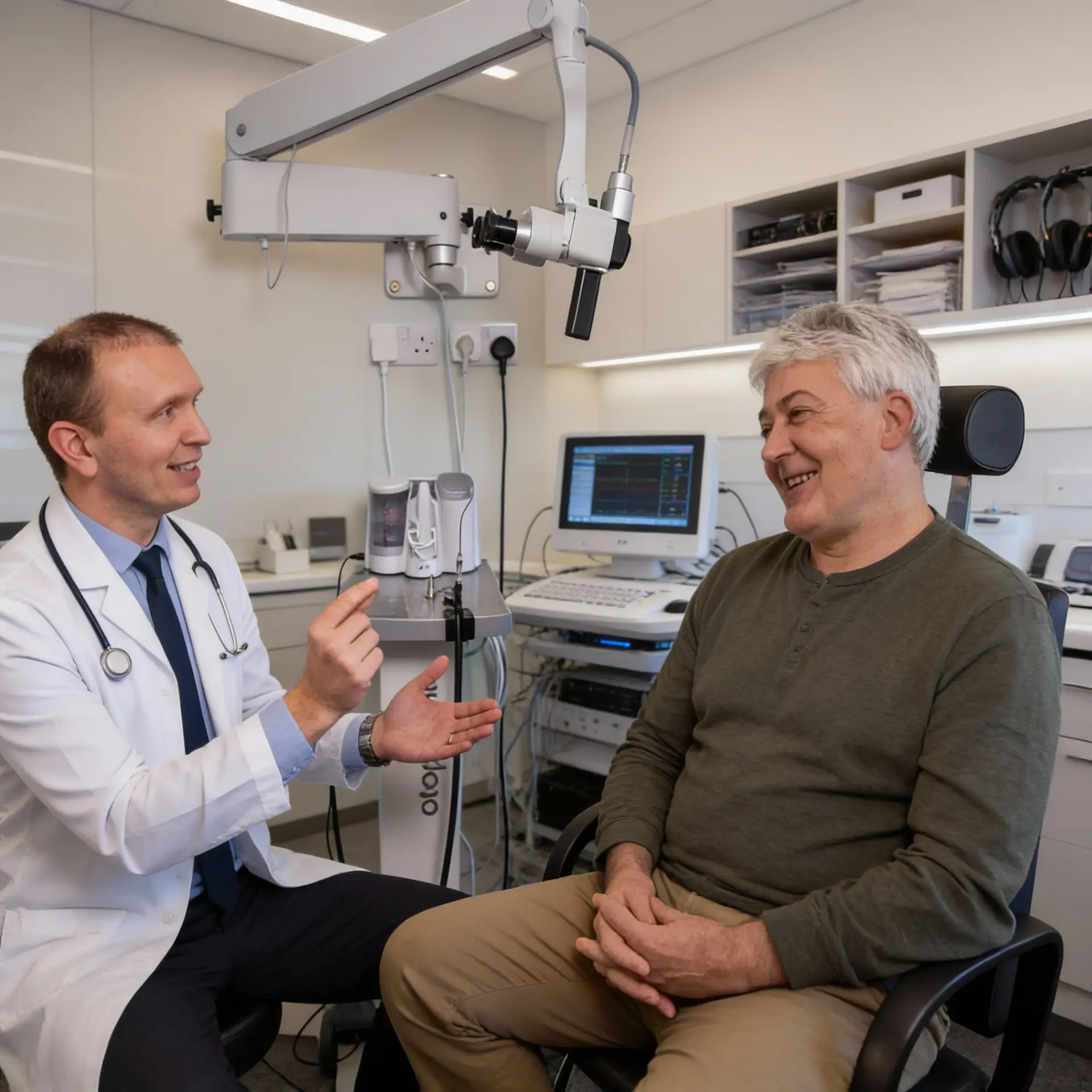
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
Specialist Tests to Assess Hearing, Balance and Inner Ear Health
FAQS
Common Questions for Pulsatile Tinnitus

Find answers to pulsatile tinnitus, treatment options, and how our specialists can help. If you have any further queries, our team at Harley Street Audiovestibular Clinic is here and happy to help.
What Is Pulsatile Tinnitus?
Pulsatile tinnitus is usually not heard by others (like in objective tinnitus) and is typified by:
A beating or throbbing sound in the ear, often in sync with your pulse.
A sense of fullness or pressure inside the ear or ears.
Issues with your balance or outright dizziness.
Hearing loss in one or both ears.
Migraines or headaches.
Sounds that get louder when you lay down to sleep.
If you are experiencing any of the above, or a beating sound that gets louder during strenuous exercise, you may be experiencing pulsatile tinnitus. If so it is important that you seek professional help in order to obtain a proper diagnosis and to explore treatment options.
What Causes Pulsatile Tinnitus?
There are many more serious causes of pulsatile tinnitus compared to other types of tinnitus. Known causes include:
Brain and Neck Blood vessel aneurysms
Arterio-venous malformation – an abnormal connection between blood vessels.
Hypertension (high blood pressure).
Problems with the thyroid gland.
Misshapen blood vessels in the ear.
Anaemia
Head and neck tumours.
Atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries in the ear).
Treatment Options
If you are diagnosed with pulsatile tinnitus, treatment will typically involve addressing the cause. Effective treatment of the cause can sometimes result in a cessation of the sounds. If the sound has not abated after the initial treatment additional treatments may be recommended, including:
A wearable sound generator.
White noise apps.
A combination of sound therapy and counselling known as “tinnitus retraining”.
Harley Street Specialists in Hearing, Dizziness & Balance
Specialist Care for Pulsatile Tinnitus
Every Pulsatile Tinnitus case is different. Your consultant will create a tailored plan to address your specific symptoms and lifestyle – when it started, how it affects your day, and which tests and treatments are right for you.